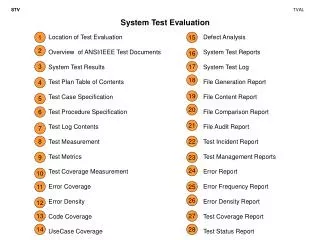
The First Amendment’s 5 Freedoms
130 likes | 492 Views
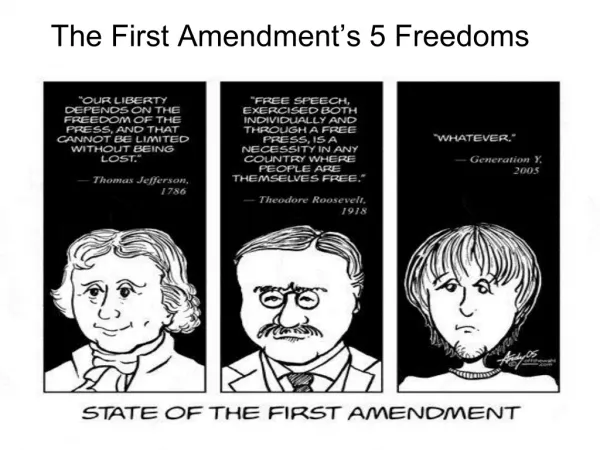
The First Amendment’s 5 Freedoms. What are the Five Freedoms?. Congress shall make no law…respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof… …or abridging the freedom of speech… …or the press…. What are the Five Freedoms?.

The First Amendment’s 5 Freedoms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What are the Five Freedoms? • Congress shall make no law…respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof… • …or abridging the freedom of speech… • …or the press…
What are the Five Freedoms? • …or the right of the people peaceably to assemble… • …and to petition the government for a redress of grievances.
Critical ? How and why do the First Amendment’s five freedoms matter in your life?
Violation or No Violation? NO • John’s parents make him go to church with them, even though he doesn’t want to go. • Chris’s friends stop inviting him out with them because all he ever does is argue about politics. • Melissa’s editor won’t let her publish a political cartoon in the school paper because the cartoon mocks the President and the editor supports the President’s policies. • Miguel’s neighbor won’t let Miguel’s “Young Democrats” group meet on his (neighbor) property. • The principal at Aliya’s private school will not allow students to gather signatures for a petition during school hours. NO NO NO NO
Violation or No Violation? YES 6. John is arrested for not attending church on Sunday, as required by state law. 7. Chris gets fined for expressing political views not approved by the government. 8. Melissa gets thrown in jail for publishing a political cartoon that mocks the President. 9. Miguel is arrested for belonging to the “Young Democrats” group. 10. Aliya is arrested for attempting to circulate a petition around her neighborhood. YES YES YES YES
#1 Supreme Court Case Students in a public school want to have a Bible Club after school, but administrators turn down their request, even though other student groups meet after school. Which freedom of the 1st Amendment? Violation or no violation? What did the court rule? Good News Club v. Milford Central School (2001)Religious clubs were allowed to meet in public schools after class hours as other clubs were permitted to do. Allowing religious clubs to meet did not violate the Establishment Clause.
#2 Supreme Court Case A public middle school student is suspended for wearing a black armband in protest of a war. Which freedom of the 1st Amendment? Violation or no violation? What did the court rule? Tinker v. Des Moines (1969)The Court ruled that students wearing black armbands to protest the Vietnam War was “pure speech,” or symbolic speech protected by the First Amendment.
#3 Supreme Court Case A town refuses to grant a parade permit to the National Socialist (Nazi) Party. Which freedom of the 1st Amendment? Violation or no violation? What did the court rule? Village of Skokie vs. National Socialist Party (1978)The National Socialist (Nazi) Party could not be prohibited from marching peacefully because of the content of their message.
#4 Supreme Court Case A high school newspaper decides to publish an article written by a student that is pro abortion. The principal immediately stops this article from being in the paper. Which freedom of the 1st Amendment? Violation or no violation? What did the court rule? Hazelwood School District v. Kuhlmeier (1988)Public school officials can censor school-sponsored newspapers, because the newspapers are part of the school curriculum rather than a forum for public expression.
#5 Supreme Court Case The state of Alabama stopped the NAACP, a civil rights group, from requesting African American’s to sit on juries during school segregation trials. Which freedom of the 1st Amendment? Violation or no violation? What did the court rule? NAACP v. Button (1963)States could not stop the NAACP from soliciting people to serve as litigants in federal court cases challenging segregation
Wrap – Up ?’s 11. Critical ? Once again, how and why do the First Amendment’s five freedoms matter in your life? How has your answer changed? 12. Why do you think the five freedoms are sometimes called “freedom of expression?” 13. What responsibilities accompany these rights? For example, does freedom of speech mean you should say whatever comes to mind at any time? Explain. 14. The First Amendment doesn’t list rights; instead it lists things the government can’t do. Why is this important? 15. Would it be possible to be free without the rights protected by the First Amendment? Why or why not?