Pathophysiology of CHF
350 likes | 850 Views
Pathophysiology of CHF. CHF. What is CHF? Fix the underlying problem Heart is a 2 sided pump Both sides can fail independent of each other. CHF. What different types of pathophysiology cause it? Systolic Dysfunction Diastolic Dysfunction High Output States. CHF.

Pathophysiology of CHF
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHF • What is CHF? • Fix the underlying problem • Heart is a 2 sided pump • Both sides can fail independent of each other.
CHF • What different types of pathophysiology cause it? • Systolic Dysfunction • Diastolic Dysfunction • High Output States
CHF • Systolic Dysfunction – What is it? Is it only related to events that occur in Systole? -1. Decreased Contractility - a. Loss of Myocytes - b. Over-stretched Heart -2. Increased Afterload - a. Increased BP - b. Stenotic Valve - Pulmonic Valve and carcinoid syndrome – 5HIAA
CHF • Diastolic Dysfunction – What is it? • 1. Impaired Relaxation • 2. Obstruction to filling • Can systolic and diastolic functions coexist?
CHF • Pressure volume loops are used to distinguish between systolic vs. diastolic dysfunction
CHF • High Output States – What is it? • Paget’s Disease • Anemia • Thiamine Deficiency • Hyperthyroidism
CHF • The failing heart and how it compensates • What does a failing heart mean, and what is decompensation? What does a failing heart look like? • Compensations made by a failing heart • Frank Starling Forces • Neuro-Hormonal Changes • Ventricular Remodeling
CHF Compensations • Frank Starling • Length Tension Mechanism
CHF Compensations • L sided failure and Frank • Blood is not going to go forward • Blood is going to back up into L atrium and pulmonary venous circulation • L Atrium, what happens when it distends?
CHF Compensations • Hoarseness:
CHF Compensations • L sided Failure and Frank • Blood eventually backs up into the pulmonary circulation • What happens there? • What’s the deal with Frank Starling Forces?
CHF Compensation • L sided failure and the lungs continued… • Pulmonary congestion
CHF Compensation • L sided failure and lungs continued… • Pulmonary Hypertension • Does pulmonary hypertension happen immediately?
L sided Compensation • L sided failure and CXR • Cephalization • Indistinct vessels, Kerly B-Lines • Whited Out lungs fields
CHF Compensations • L sided failure symptoms related to congestion • Blood not going forward: • Muscle fatigue • Confusion • Blood going backwards: • Atrial Distension • Arrhythmias • Thrombus formation • Hoarseness • Mitral Regurgitation • S3
CHF Compensations • L sided failure symptoms continued… • Blood going backwards continued… • Pulmonary congestion • Pulmonary edema • Pulmonary hypertension – R sided failure • Dyspnea, Dyspnea at night • Nocturnal enuresis • Orthopnea • Cardiac Asthma • Hypoxia, cyanosis
CHF Compensations • R sided failure and Frank: • Most Common Cause is? • Cor pulmonale? • Blood is going to eventually back up into the R atrium and systemic and portal venous circulation.
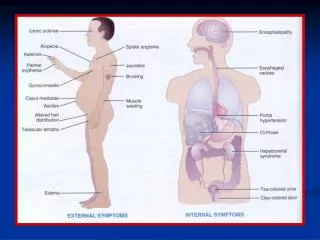
CHF Compensations • What happens when this blood backs up? • Liver Congestion • Gastrointestinal Tract Nutmeg Liver
CHF Compensations • What happens when this blood backs up continued… • Pitting Edema • Frank Starling Forces • Stasis Dermatitis • P02?
CHF Compensations • JVD – jugular venous pressure chart
CHF Compensations • Acute R sided failure • Causes? • Would you expect to see any change to the R ventricle?
CHF Compensations • R sided failure symptoms from the backing up of blood: • Pitting Edema • JVD • GI discomfort • Liver congestion • RUQ pain • Hepatojugular Reflex • Ascites – Puddle sign
CHF complications • Would you expect someone with R sided failure only, that is, no L sided failure, to have pulmonary hypertension or pulmonary edema?
CHF Compensations • Neurohormonal changes: • Renin-Angiotensin System • Adrenergic System • ADH
CHF Compensations • Renin-Angiotensin System – raise EABV, and lower plasma oncotic p.
CHF Compensations • Does the Renin-Angiotensin System restore EABV back to normal? • Why is this harmful in the end?
CHF Compensations • Adrenergic System: • Increased Sympathetic outflow • Increased effects of epinephrine on adrenergic receptors throughout your body • What pathological process could keep the adrenergic system on even if the EABV is restored?
CHF Compensations • Does the adrenergic system restore the EABV? • Why is this harmful in the end?
CHF Compensations • ADH secretion • Why do its effects become blunted in long run?
CHF Compensations • Ventricular Remodeling