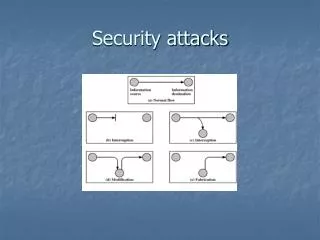
Network Security Measures Against Layer 2 Attacks
330 likes | 404 Views
Explore MAC attacks, DHCP vulnerabilities, and ARP threats, along with security solutions like port security and ARP inspection to safeguard your network from malicious actors.

Network Security Measures Against Layer 2 Attacks
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MAC Attacks • MAC Flooding overflows the switch MAC address table (CAM) forcing the switch to forward frames to all ports on a VLAN (much like a hub) • MACOF tool generates random MAC/IP address combinations in order to overflow the CAM table
MAC Security • Port Security limits the number of MAC addresses that can be learned on a single port, preventing MAC flooding • Learning MAC • static – manually configured, saved in startup config (copy run start) • sticky – automatically learned, added to running config, (saved w/copy run start) • dynamic – automatically learned, not saved • MAC • counters – number of MACs allowed • timers – how long to remember MAC(s) • Violation actions • protect – drop traffic from unknown MACs when over limit • restrict – drop traffic from unknown MACs when over limit and send alarm • shutdown – shutdown port with errdisable
No Port Security Enabled: interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate spanning-tree portfast Before MACOF attack: Layer2-Switch#sh mac address-table count Mac Entries for Vlan 10: --------------------------- Dynamic Address Count : 1 Static Address Count : 1 Total Mac Addresses : 2 Total Mac Address Space Available: 6078
After MACOF attack: Layer2-Switch#sh mac address-table count Mac Entries for Vlan 10: --------------------------- Dynamic Address Count : 6079 Static Address Count : 1 Total Mac Addresses : 6080 Total Mac Address Space Available: 0
Port Security Enabled: interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate switchport port-security maximum 3 switchport port-security switchport port-security aging time 2 switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security aging type inactivity spanning-tree portfast Before MACOF attack: Layer2-Switch#sh port-security Secure Port MaxSecureAddr CurrentAddr SecurityViolation Security Action (Count) (Count) (Count) --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Gi1/0/1 3 1 0 Restrict Gi1/0/2 3 0 0 Restrict --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 2 Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 6272
During and After MACOF attack: Layer2-Switch#sh mac address-table count Mac Entries for Vlan 10: --------------------------- Dynamic Address Count : 1 Static Address Count : 4 Total Mac Addresses : 5 Total Mac Address Space Available: 6075 Layer2-Switch#sh port-security Secure Port MaxSecureAddr CurrentAddr SecurityViolation Security Action (Count) (Count) (Count) --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Gi1/0/1 3 3 67556 Restrict Gi1/0/2 3 0 0 Restrict --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total Addresses in System (excluding one mac per port) : 2 Max Addresses limit in System (excluding one mac per port) : 6272
DHCP Attacks • DHCP Starvation is a DOS attack which prevents valid hosts from getting Dynamic IP configuration • A Rogue DHCP server is used to pass invalid IP configuration information to valid hosts
DHCP Security • DHCP Exhaustion can be prevented with the same port security measures used to protect against MAC flooding • Rogue DHCP servers can be eliminated with the use of DHCP Snooping where all DHCP request and replies are tracked and rate limited • Valid DHCP server ports must be ‘trusted’
ARP Attacks • ARP Poisoning is used to alter ARP entries in a switch and on hosts • This allows an attacker to send gratuitous ARP replies redirecting traffic from hosts on the VLAN through his machine
ARP Security • Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) is used to prevent ARP poisoning • DAI uses information in the DHCP snooping table to ensure invalid ARP packets are dropped and ARP packets are rate limited • With both DHCP snooping and DAI static entries can be built for non-DHCP devices
No DAI Enabled: Before ARP poisoning: PC: C:\>arp -a Interface: 1.1.1.3 --- 0x10003 Internet Address Physical Address Type 1.1.1.1 00-14-69-f2-04-41 dynamic 1.1.1.2 00-14-22-b4-98-6f dynamic 1.1.1.254 00-11-20-27-a6-c0 dynamic Switch: Layer2-Switch#sh arp Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 1.1.1.1 - 0014.69f2.0441 ARPA Vlan10 Internet 1.1.1.3 2 0006.5b17.9900 ARPA Vlan10 Internet 1.1.1.254 0 0011.2027.a6c0 ARPA Vlan10
During ARP poisoning: PC: C:\>arp -a Interface: 1.1.1.3 --- 0x10003 Internet Address Physical Address Type 1.1.1.1 00-14-22-b4-98-6f dynamic 1.1.1.2 00-14-22-b4-98-6f dynamic 1.1.1.254 00-14-22-b4-98-6f dynamic Switch: Layer2-Switch#sh arp Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 1.1.1.1 - 0014.69f2.0441 ARPA Vlan10 Internet 1.1.1.3 0 0014.22b4.986f ARPA Vlan10 Internet 1.1.1.254 0 0014.22b4.986f ARPA Vlan10 Telnet Example from Ettercap: TELNET: 1.1.1.1:23 -> USER: admin PASS: cisco
DAI Enabled: ip dhcp snooping vlan 10 ip dhcp snooping database flash:dhcpsnooping.db ip dhcp snooping ip arp inspection vlan 10 ip arp inspection validate src-mac dst-mac ip ip arp inspection log-buffer entries 1024 ip arp inspection log-buffer logs 1024 interval 10 interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate switchport port-security maximum 3 switchport port-security switchport port-security aging time 2 switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security aging type inactivity ip arp inspection limit rate 25 spanning-tree portfast ip verify source ip dhcp snooping limit rate 25
During ARP poisoning: PC: C:\>arp -a Interface: 1.1.1.3 --- 0x10003 Internet Address Physical Address Type 1.1.1.1 00-14-69-f2-04-41 dynamic 1.1.1.2 00-14-22-b4-98-6f dynamic 1.1.1.254 00-11-20-27-a6-c0 dynamic Switch: Layer2-Switch#sh arp Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 1.1.1.1 - 0014.69f2.0441 ARPA Vlan10 Internet 1.1.1.3 0 0006.5b17.9900 ARPA Vlan10 Internet 1.1.1.2 4 0014.22b4.986f ARPA Vlan10 Internet 1.1.1.254 3 0011.2027.a6c0 ARPA Vlan10 Layer2-Switch#sh log 1d00h: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING_DENY: 2 Invalid ARPs (Res) on Gi1/0/1, vlan 10. ([0014.22b4.986f/1.1.1.3/0011.2027.a6c0/1.1.1.254/00:14:53 UTC Tue Mar 2 1993]) 1d00h: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING_DENY: 2 Invalid ARPs (Res) on Gi1/0/1, vlan 10. ([0014.22b4.986f/1.1.1.254/0006.5b17.9900/1.1.1.3/00:14:53 UTC Tue Mar 2 1993]) 1d00h: %SW_DAI-4-DHCP_SNOOPING_DENY: 2 Invalid ARPs (Res) on Gi1/0/1, vlan 10. ([0014.22b4.986f/1.1.1.1/0011.2027.a6c0/1.1.1.254/00:14:53 UTC Tue Mar 2 1993])
Spoofing Attacks • MAC Spoofing • IP Spoofing • Spoofing is a method of using the MAC or IP address of another device and then assuming the privilege level of that device
Spoofing Security • IP Source Guard prevents both MAC and IP address spoofing using info from the DHCP snooping table • Preventing MAC spoofing requires specific option 82 to be assigned by DHCP server (Cisco Registrar, Cisco IOS and Avaya DHCP server can do this) • Preventing IP spoofing has no other requirements and is configured per port
No IP Source Guard Enabled: interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate switchport port-security maximum 3 switchport port-security switchport port-security aging time 2 switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security aging type inactivity ip arp inspection limit rate 25 spanning-tree portfast ip dhcp snooping limit rate 25
Debug of IP spoofing attack: Layer2-Switch#debug ip icmp ICMP packet debugging is on Layer2-Switch# From attacker machine (1.1.1.2) not spoofing: nemesis icmp -S 1.1.1.2 -D 1.1.1.1 On Switch: Layer2-Switch# 1d00h: ICMP: echo reply sent, src 1.1.1.1, dst 1.1.1.2 From attacker machine (1.1.1.2) spoofing 10.48.1.1: nemesis icmp -S 10.48.1.1 -D 1.1.1.1 On Switch: Layer2-Switch# 1d00h: ICMP: echo reply sent, src 1.1.1.1, dst 10.48.1.1
IP Source Guard Enabled: interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access switchport nonegotiate switchport port-security maximum 3 switchport port-security switchport port-security aging time 2 switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security aging type inactivity ip arp inspection limit rate 25 spanning-tree portfast ip verify source ip dhcp snooping limit rate 25
Debug of IP spoofing attack: Layer2-Switch#debug ip icmp ICMP packet debugging is on Layer2-Switch# From attacker machine (1.1.1.2) not spoofing: nemesis icmp -S 1.1.1.2 -D 1.1.1.1 On Switch: Layer2-Switch# 1d00h: ICMP: echo reply sent, src 1.1.1.1, dst 1.1.1.2 From attacker machine (1.1.1.2) spoofing 10.48.1.1: nemesis icmp -S 10.48.1.1 -D 1.1.1.1 On Switch: [nothing]
Other Notables • HSRP/GLBP Authentication • Routing Protocol Authentication • Storm Control