Vocabulary Instruction
340 likes | 745 Views
Vocabulary Instruction. Strategies for Word Meaning, Not Word Memorization. Literacy Vision Statement.

Vocabulary Instruction
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Vocabulary Instruction Strategies for Word Meaning, Not Word Memorization
Literacy Vision Statement Aiken County Public Schools demonstrates an unwavering commitment of the educational community to embrace their responsibility for ensuring that each student at any level becomes a successful reader and writer.
Word Study Phonics skills Spelling patterns Vocabulary Instruction Word meaning Contextual framework What’s the difference?
“Group Chat” • Why do we teach vocabulary? • What is our ultimate goal in vocabulary instruction? Our answers to these questions should be the guiding force of how we structure our vocabulary instruction…
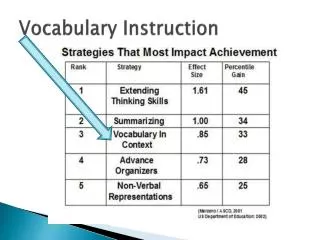
What The Research Says The scientific research on vocabulary instruction reveals that (1) most vocabulary is learned indirectly, and (2) some vocabulary must be taught directly. The following conclusions about indirect vocabulary learning and direct vocabulary instruction are of particular interest and value to classroom teachers: Children learn the meanings of most words indirectly, through everyday experiences with oral and written language. Although a great deal of vocabulary is learned indirectly, some vocabulary should be taught directly. National Reading Panel
Context clues “Would you…” cards Making Choices Word Splash! Is/Is Not Whole/Part/Whole diagrams Picture cards Concept Cards Graffiti Walls Charades Categories Ordering Words Constructing Words (prefixes, suffixes) Selecting Words (prefixes, suffixes) Multiple Meaning Maps Probable Passage Strategies to Discuss
Model for students how they can “break free” of the dictionary through Shared Reading, read alouds, small group instruction, Independent Reading, etc.
“Would You Rather…” Cards (Beck, McKeown, Kucan, 2002)
I’ll say some things. If they would be considered “quiet”, put a thumbs up: Going to church Going to a football game Going to sleep Riding a roller coaster I’ll say some things. If they would be considered “ferocious”, put a thumbs up: A quiet kitten A roaring lion A thundering storm Making Choices (Beck, McKeown, Kucan, 2002)
Word Splash • Select a few key words from the text • Put words on chart paper or Smartboard • Students write what they know about a word prior to reading text • Students write what they learned about the word after reading the text
“Tacky The Penguin” Odd Companion “Thank You Ma’m” Bully Victim Frail Word Splash
Teacher Prep- Divides sentence strip into three sections Pre-selects words to be studied and writes word in middle on sentence strip (students can also select words from their own reading to do a sentence strip on) Writes “Is” (synonym) on left section of sentence strip and “Is Not” (antonym) on right side Students- Reads book that contains word being studied Writes a synonym for the word on the left side of the sentence strip Writes an antonym for the word on the right side of the sentence strip Illustrates “Is” and “Is Not” words Is/Is Not Vocabulary Strips Is Is Not frail
Whole/Part/Whole Diagrams • Select a word: compound, prefix, suffix • Write word at top of paper • Write what the parts of the word mean • Puts the meaning of the parts together to form a definition
Picture Cards • Write a word on the front of an index card • Draw a picture on the back of the card • Write a simple definition of the word
Charades • Select key vocabulary words from the text and put on index cards • Give 1 card to a small group of students • Students spend 3-4 minutes preparing how to silently act out the word • Students act out word in front of class • Class guesses the word • Students tell WHY they acted the way they did
Mammal Bear Dog Cat Horse Mammal Bear Dog Cat Horse Categories Tax • Tea Act • Sugar Act • Stamp Act Tax • Tea Act • Sugar Act • Stamp Act
Boil Simmer Explode Toss Throw Hurl “Word Scales” Words • Odd • Different • Unique • Mad • Upset • Furious
Constructing Words • Index cards of prefixes, suffixes, and root words selected from previously read text • Put cards in a plastic bag • Students match the prefix and/or suffix with the root word • Students use the text to find the word and discuss/write how it was used • Students can write their own sentence using the constructed word Mis happy Un behaving ful Joy
Selecting Words • A person who is acting poorly is:misbehaving, misled, mistreated • A person who is always ready for anything is: predicted, prepared, prevented
Multiple Meaning Maps • My brother caught the bug in his insect net. • My brother really bugs me when he sings loudly in the shower! bug
Multiple Meaning Maps • Driving on a highway) There's a tollbridge ahead. Do you have any quarters? • The highway death tollhas declined sharply since police began to enforce the drunk driving laws more aggressively. • The bell in the old church tower tolledfour o'clock. Toll
Kindergarten & 1st 2nd and 3rd 4th and 5th (Beers, 2003)
References • Beck, I., McKeown, L., Kucan, L., (2002). Bringing word to life: Robust vocabulary instruction. New York, NY; Gillford Press. • Beer, K., (2003). When kids can’t read: What teachers can do. Portsmouth, NH; Heinemann. • http://people.bu.edu/jpettigr/Artilces_and_Presentations/Vocabulary.htm